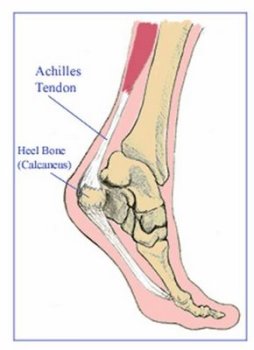
Overview

Your foot is made up of 26 bones, 33 joints, and more than 100 tendons. The heel is the largest bone in your foot. If you overuse or injure your heel, you may experience Heel Pain. This can range from mild to disabling. In many cases, if you have heel pain, you will need a doctor to diagnose the cause.
Causes
Heel pain can have many causes but the vast majority is caused by plantar fasciitis. Plantar means, ?bottom of the foot.? Fascia is a ligament or ?bundle? of ligaments. The plantar fascia is the thick ligament that helps to hold up the foot and provide spring in our step. Plantar fasciitis is an inflammation of the plantar fascia and causes more than 90% of heel pain among adults in the US. Plantar fasciitis can be acute, that is, as simple strain of the ligament but often is chronic, hanging on for months if not years. Why does that happen? The answer is poor foot mechanics, the foot sinking down too far allowing the plantar fascia to overstretch with each step taken.
Symptoms
Initially, this pain may only be present when first standing up after sleeping or sitting. As you walk around, the muscle and tendon loosen and the pain goes away. As this problem progresses, the pain can be present with all standing and walking. You may notice a knot or bump on the back of the heel. Swelling may develop. In some cases, pressure from the back of the shoe causes pain.
Diagnosis
Your GP or podiatrist (a healthcare professional who specialises in foot care) may be able to diagnose the cause of your heel pain by asking about your symptoms and examining your heel and foot. You will usually only need further tests if you have additional symptoms that suggest the cause of your heel pain is not inflammation, such as numbness or a tingling sensation in your foot – this could be a sign of nerve damage in your feet and legs (peripheral neuropathy), your foot feels hot and you have a high temperature (fever) of 38C (100.4F) or above – these could be signs of a bone infection, you have stiffness and swelling in your heel – this could be a sign of arthritis. Possible further tests may include, blood tests, X-rays – where small doses of radiation are used to detect problems with your bones and tissues, a magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scan or ultrasound scan, which are more detailed scans.
Non Surgical Treatment
Treatment for plantar fasciitis – the vast majority of patients recover with conservative treatments (designed to avoid radical medical therapeutic measures or operative procedures) within months. Heel with ice-pack. Home care such as rest, ice-pack use, proper-fitting footwear and foot supports are often enough to ease heel pain. Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) – medications with analgesic (pain reducing), antipyretic (fever reducing) effects. In higher doses they also have anti-inflammatory effects, they reduce inflammation (swelling). Non-steroidal distinguishes NSAIDs from other drugs which contain steroids, which are also anti-inflammatory. NSAIDs are non-narcotic (they do not induce stupor). For patients with plantar fasciitis they may help with pain and inflammation. Corticosteroids, a corticosteroid solution is applied over the affected area on the skin; an electric current is used to help absorption. Alternatively, the doctor may decide to inject the medication. However, multiple injections may result in a weakened plantar fascia, significantly increasing the risk of rupture and shrinkage of the fat pad covering the heel bone. Some doctors may use ultrasound to help them make sure they have injected in the right place Corticosteroids are usually recommended when NSAIDs have not helped. Physical therapy, a qualified/specialized physical therapist (UK: physiotherapist) can teach the patient exercises which stretch the plantar fascia and Achilles tendon, as well as strengthening the lower leg muscles, resulting in better stabilization of the ankle and heel. The patient may also be taught how to apply athletic taping, which gives the bottom of the foot better support. Night splints, the splint is fitted to the calf and foot; the patient keeps it on during sleep. Overnight the plantar fascia and Achilles tendon are held in a lengthened position; this stretches them. Orthotics, insoles and orthotics (assistive devices) can be useful to correct foot faults, as well as cushioning and cradling the arch during the healing process. Extracorporeal shock wave therapy, sound waves are aimed at the affected area to encourage and stimulate healing. This type of therapy is only recommended for chronic (long-term) cases, which have not responded to conservative therapy.
Surgical Treatment
When a diagnosis of plantar fasciitis is made early, most patients respond to conservative treatment and don?t require surgical intervention. Often, when there is a secondary diagnosis contributing to your pain, such as an entrapped nerve, and you are non-responsive to conservative care, surgery may be considered. Dr. Talarico will discuss all options and which approach would be the most beneficial for your condition.
Prevention

Flexibility is key when it comes to staving off the pain associated with these heel conditions. The body is designed to work in harmony, so stretching shouldn?t be concentrated solely on the foot itself. The sympathetic tendons and muscles that move the foot should also be stretched and gently exercised to ensure the best results for your heel stretches. Take the time to stretch thighs, calves and ankles to encourage healthy blood flow and relaxed muscle tension that will keep pain to a minimum. If ice is recommended by a doctor, try freezing a half bottle of water and slowly rolling your bare foot back and forth over it for as long as is comfortable. The use of elastic or canvas straps to facilitate stretching of an extended leg can also be helpful when stretching without an assistant handy. Once cleared by a doctor, a daily regimen of over-the-counter anti-inflammatory medication like Naproxen Sodium will keep pain at bay and increase flexibility in those afflicted by heel pain. While this medication is not intended to act as a substitute for medical assessments, orthopedics or stretching, it can nonetheless be helpful in keeping discomfort muted enough to enjoy daily life. When taking any medication for your heel pain, be sure to follow directions regarding food and drink, and ask your pharmacist about possible interactions with existing medications or frequent activities.
 Achilles tendinitis is very common among running athletes. The calf muscles attach to the calcaneus via the Achilles tendon. During running, the calf muscles help with the lift-off phase of gait. Repetitive forces from running combined with insufficient recovery time can initially cause inflammation in the tendon paratenon (fatty areolar tissue that surrounds the tendon). A complete tear of the Achilles tendon is a serious injury, usually resulting from sudden, forceful stress. Tendon tears can occur with minimal exertion in people who have taken fluoroquinolone antibiotics.
Achilles tendinitis is very common among running athletes. The calf muscles attach to the calcaneus via the Achilles tendon. During running, the calf muscles help with the lift-off phase of gait. Repetitive forces from running combined with insufficient recovery time can initially cause inflammation in the tendon paratenon (fatty areolar tissue that surrounds the tendon). A complete tear of the Achilles tendon is a serious injury, usually resulting from sudden, forceful stress. Tendon tears can occur with minimal exertion in people who have taken fluoroquinolone antibiotics.